mott scattering polarimeter|mott polarimetry : solutions The cylindrical or spherical geometries of the compact polarimeters, shown in Figs. 3(a) and 3(b), respectively, allow inelastic scattering events to be elim inated electrostatically with a . webAs apostas esportivas da 1991Bet agora estão disponíveis! 🔥 Na plataforma esportiva da 1991Bet oferecemos não apenas uma variedade de eventos esportivos, mas também .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEB18+ Garotas de Programa em Piraquara | Acompanhantes em Piraquara. Conheça lindas acompanhantes em Piraquara agora! Veja fotos, vídeos e whatsapp de garotas de .
The calibration of Mott polarimeters is discussed together with the potential sources of systematic error that can arise and that can limit measurement accuracies. The aim is to present a comprehensive practical guide to Mott polarimetry and the capabilities of the .The calibration of Mott polarimeters is discussed together with the potential .Institutional librarians/administrators: Please visit Library Resource Center for the .Today polarimeters based on Mott scattering (or, more simply, Mott polarimeters) are extensively used in atomic and molecular, solid state, nuclear, and high-energy physics. This use results .
The cylindrical or spherical geometries of the compact polarimeters, shown in Figs. 3(a) and 3(b), respectively, allow inelastic scattering events to be elim inated electrostatically with a . In two separate series of measurements from two different photocathode electron sources, we have measured the Mott scattering asymmetries produced by an approximately .
In the Mott polarimeter, high-energy electrons are scattered on a target film com-posed of heavy atoms such as Au or Th, (so-called Mott scattering) and captured by electron detectors that . A Mott electron polarimeter for the Mainzer microtron (MAMI) accelerator in Mainz, Germany is developed, demonstrating that the results of asymmetry measurements are .

A compact classical electron spin detector based on Mott scattering is described. This Mott polarimeter has an efficiency of ≈5.6×10 −4, a maximum counting rate of 500 kcps . Electron polarimeters based on Mott scattering are extensively used in atomic and molecular, solid state, nuclear, and high‐energy physics. This use stems from the increasing realization. Mott polarimetry takes advantage of the asymmetry generated when a transversely polarized electron scatters from an unpolarized large Z nucleus. The asymmetry .
Electron polarimeters based on Mott scattering are extensively used in atomic and molecular, solid state, nuclear, and high‐energy physics. This use stems from the increasing realization that much additional information concerning many physical processes can be obtained through spin‐dependent measurements. In this review we discuss the basic physics and . Electron polarimeters based on Mott scattering are extensively used in atomic and molecular, solid state, nuclear, and high‐energy physics. . A number of different Mott polarimeter designs are . The development of a conceptual design of a Compton polarimeter for the future Electron Ion Collider will also be discussed. This manuscript has been authored by Brookhaven Science Associates, LLC under Contract No. DE-SC0012704 with the U.S. Department of Energy. . The cross section for a polarized electron undergoing Mott scattering at an .
Electron polarimeters based on Mott scattering are extensively used in different fields in physics such as atomic, nuclear or particle physics [].This is because spin-dependent measurements give additional information on the physical processes under study [].Mott polarimeters are instrumental in the study of spin-dependent effects in atomic collisions, .A polarimeter [1] is a scientific instrument used to measure optical rotation: the angle of rotation caused by passing linearly polarized light through an optically active substance. [ 2 ] Some chemical substances are optically active, and linearly polarized (uni-directional) light will rotate either to the left (counter-clockwise) or right .
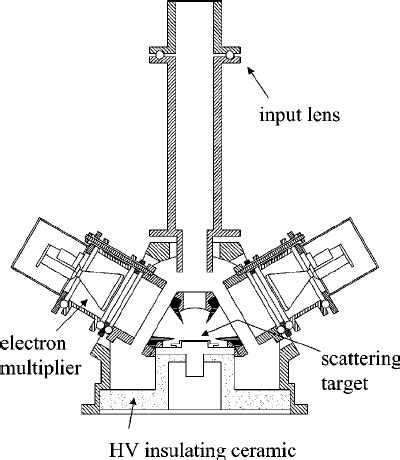
A compact classical electron spin detector based on Mott scattering is described. This Mott polarimeter has an efficiency of 5.610 4 , a maximum counting rate of 500 kcps and bulk size 15 cm25 cm.
A compact classical electron spin detector based on Mott scattering is described. This Mott polarimeter has an efficiency of ≈5.6×10 −4, a maximum counting rate of 500 kcps and bulk size 15 cm ×25 cm. The design of the polarimeter goes back to the classical Mott detector, operating from 100 to 120 kV but it can be combined with conventional analyzers due to its .The design and performance of a compact Mott detector of electron polarisation based on a concentric cylinder electrode geometry is described. Electrons accelerated in the cylindrical field are scattered from a gold foil and decelerated in the same field before detection. The resultant rejection of inelastically scattered electrons is shown to permit efficient operation of the .a compact retarding-field Mott polarimeter. The polarimeter uses simplified electrode structures and operates from 5 to 30kV. The effective Sherman function for this device has been calibrated by comparison with the CEBAF 5MeV Mott polarimeter. For elastic scattering from a thick gold target at 20keV, the effective Sherman function is 0.201(5).
mott polarimetry
comparable to the diffuse scattering polarimeter. A third type of spin polarimeter, which can be considered different from the conventional lOO-kV Mott detector,* is the com- pact Rice University-type Mott polarimeter,9’ 10 which op- erates at 2040 kV. Several factors were considered in deciding which spin
In the present Mott polarimeter, . Mott, N. F. The Scattering of Fast Electrons by Atomic Nuclei, Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series A 124, 425–442 (1929).A number of different Mott polarimeter designs are described that illustrate the wide range of operating energies (10 eV-1 MeV) and geometries . Today polarimeters based on Mott scattering (or, more simply, Mott polarimeters) are extensively used in atomic and molecular, solid state, nuclear, and high-energy physics. This use results from the . For example, a Monte Carlo simulation of the MAMI (Mainzer Mikrotron) Mott polarimeter in Geant4 has been described by Tioukine etal. [22]. It did not take into account the polarization effects, but could be easily extended to do so by using the Mott scattering model presented here, instead of the default one.
We have developed a Mott electron polarimeter for the Mainzer microtron (MAMI) accelerator in Mainz, Germany. At beam energies ranging between 1.0 and 3.5 MeV two double focusing magnet spectrometers collect elastically backscattered electrons from gold targets. In spite of the small spectrometer acceptance, a sufficient statistical efficiency .
Low energy (E{sub k} = 100 keV) Mott scattering polarimeters are ill-suited to support operations foreseen for the polarized electron injector at Jefferson Lab. One solution is to measure the polarization at 5 MeV where multiple and plural scattering are unimportant and precision beam monitoring is straightforward. The polarimeter uses simplified electrode structures and operates from 5 to 30 kV. The effective Sherman function for this device has been calibrated by comparison with the CEBAF 5 MeV Mott polarimeter. For elastic scattering from a thick gold target at 20 keV, the effective Sherman function is 0.201n], (I)The Derivation of the Mott Scattering Formula In 1911 Ernest Rutherford published a formula which indicated that the number of particles that would be deflected by an angle θ due to scattering from fixed nuclei is inversely proportional to the fourth power of the sine function of one half the angle of deflection; i.e.,
n], (I)FIG. 1. Scale drawing of standard Mott-scattering electron polarimeter (Ref. 22) (side and end views). The Wien-filter spin rotator consists of crossed transverse electric and magnetic fields of 1.91 kV /cm and 39 G, respectively. With the Wien filter maintained at +6 kV with respect to ground, the beam energy in the Wien filter is 7 keV.
Mott Scattering Scattering of a relativistic electron by a pointlike spin 1/2 proton Similar to electron muon scattering from last Lecture Usually described in the Lab frame, where the proton is at rest: θ is the lab scattering angle of the electron pe is the incident electron beam momentum q2 is the four-momentum transfer of the virtual photon
Here, a well-known polarized electron beam produced from a bulk GaAs photocathode in a dc high-voltage photogun was first measured in a 180 keV Mott scattering polarimeter, then used to characterize and calibrate the Compton transmission polarimeter as a function of the polarized target magnetization and beam properties. A simple compact retarding-potential Mott polarimeter is described that operates at an electron accelerating voltage of 25 kV. With a thorium target the instrument provides efficiencies eta [=S2eff(I/I0), where Seff is the effective asymmetry (Sherman) function and I/I0 is the scattering efficiency] of approximately 1.3 x 10(-4) which are .
mott electron polarimetry
Thus, attention is drawn again to Mott scattering, a widely used method for electron spin detection up to energies near 1 MeV. Mott electron polarimetry has been reviewed in detail [2-4]. So we restrict to recall the pioneering work of van Klinken [5], who performed a calibration of a four detector Mott polarimeter by double scattering of .
Low energy (E k =100 keV) Mott scattering polarimeters are ill-suited to support operations foreseen for the polarized electron injector at Jefferson Lab. One solution is to measure the polarization at 5 MeV where multiple and plural scattering are unimportant and precision beam monitoring is straightforward.The compact conical-type retarding Mott spin polarimeter, or micro-Mott polarimeter, is widely used and exhibits the following features:9 ~1! it is easy to operate, ~2! it has a large electron acceptance phase space, and ~3! it has a stable Sherman function. It is therefore easy to adapt a micro-Mott polarimeter to an energy analyzer for spin- The results are shown in Fig. 6. Two additional measurements were done using a Mott polarimeter [38] [39] [40][41], which is located near the injector where the beam electrons have reached 5 MeV .
WEBPasso 1: abra o iFood e selecione a aba "Perfil"; Passo 2: em seguida, vá até a aba "Ajuda"; Continua após a publicidade. Passo 3: na tela de .
mott scattering polarimeter|mott polarimetry